This post will very briefly discuss two of the computation options available in Azure Machine Learning; compute instances and compute clusters.
A Compute Instance in Azure Machine Learning is a cloud-based workstation, where all the necessary frameworks, tools and libraries are installed and configured, thus making it easy to run machine CPU or GPU based learning experiments and manage the Azure ML resources. We can create instances by selecting from one of the VM sizes available in Azure. A number of additional advanced configuration settings are available during the creation of the instance, such as the ability to schedule the time when the instance is operating and if we can access it via SSH. Once a Compute Instance is created, unless a schedule is created, it is up to the user to switch on and off the instance, so it is advisable to carefully monitor this aspect to limit the overall cost of the experiment.
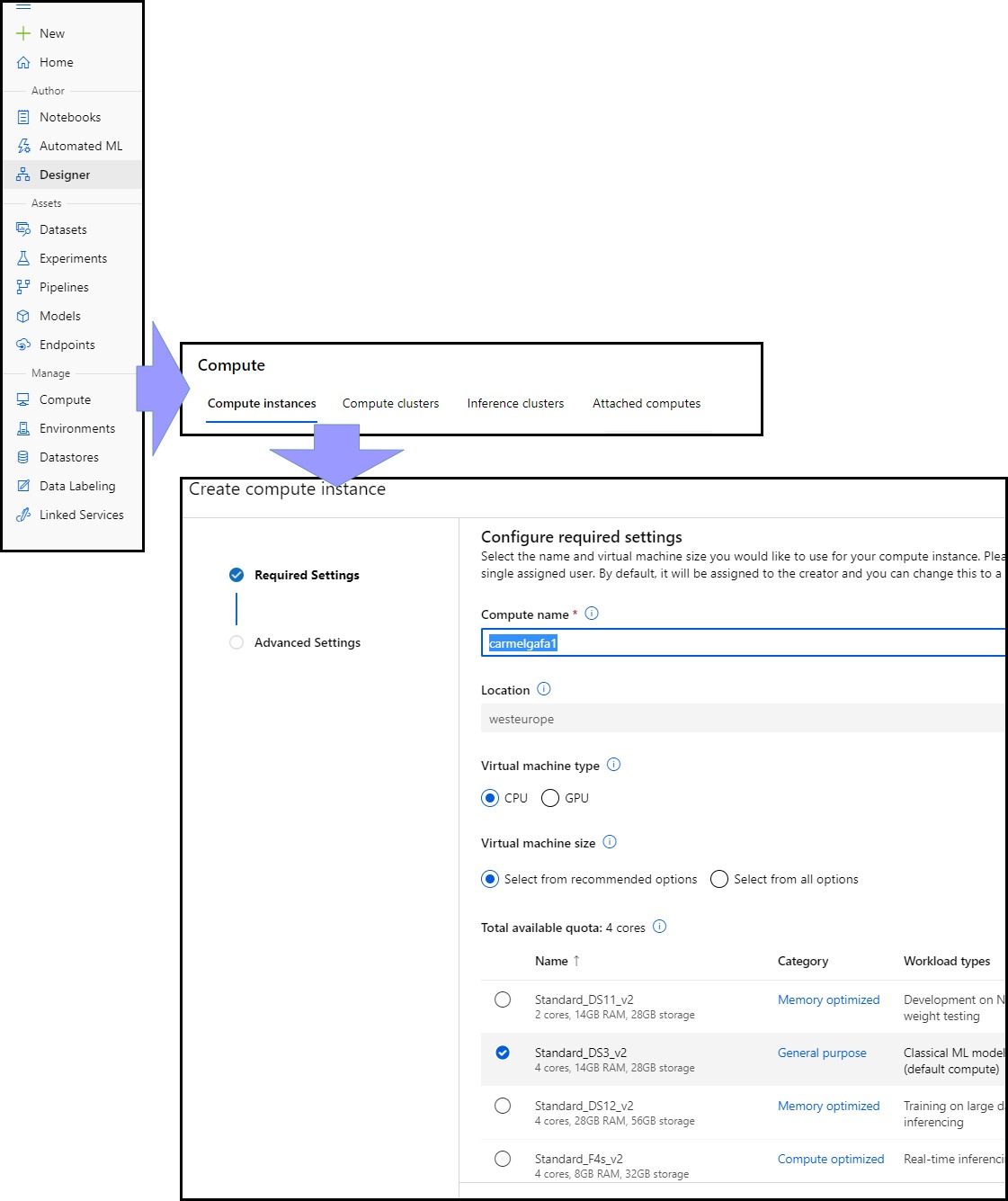
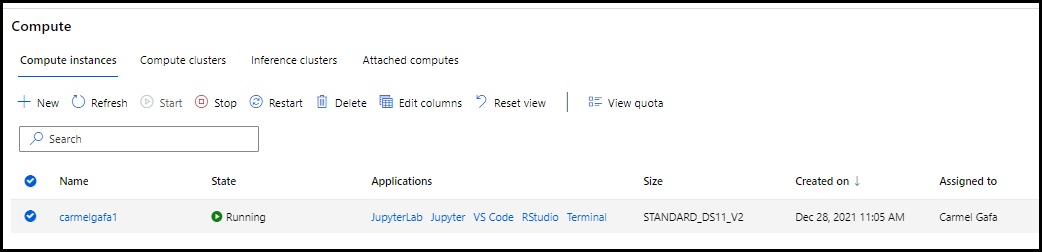
It is possible to access an Azure ML Compute Instance using several methods, namely:
- Jupyter Labs and Jupyter Notebooks
- Visual Studio Code integration
- RStudio
- terminal
For production-grade model training, Azure Machine Learning Compute Target is used. Compute targets are multi-node scaling compute resources where we can execute our training script or host our service deployment, thus making it possible to use parallel processing for such computations. We can create each node with a user-specified hardware configuration.
A critical parameter of a compute target creation is the possibility to define a cluster as dedicated or low priority. Low priority clusters are created when the resources are available, so experiments deployed on low priority clusters can take some time to commence. They are generally used for development and testing. They are, however substantially cheaper than dedicated clusters.
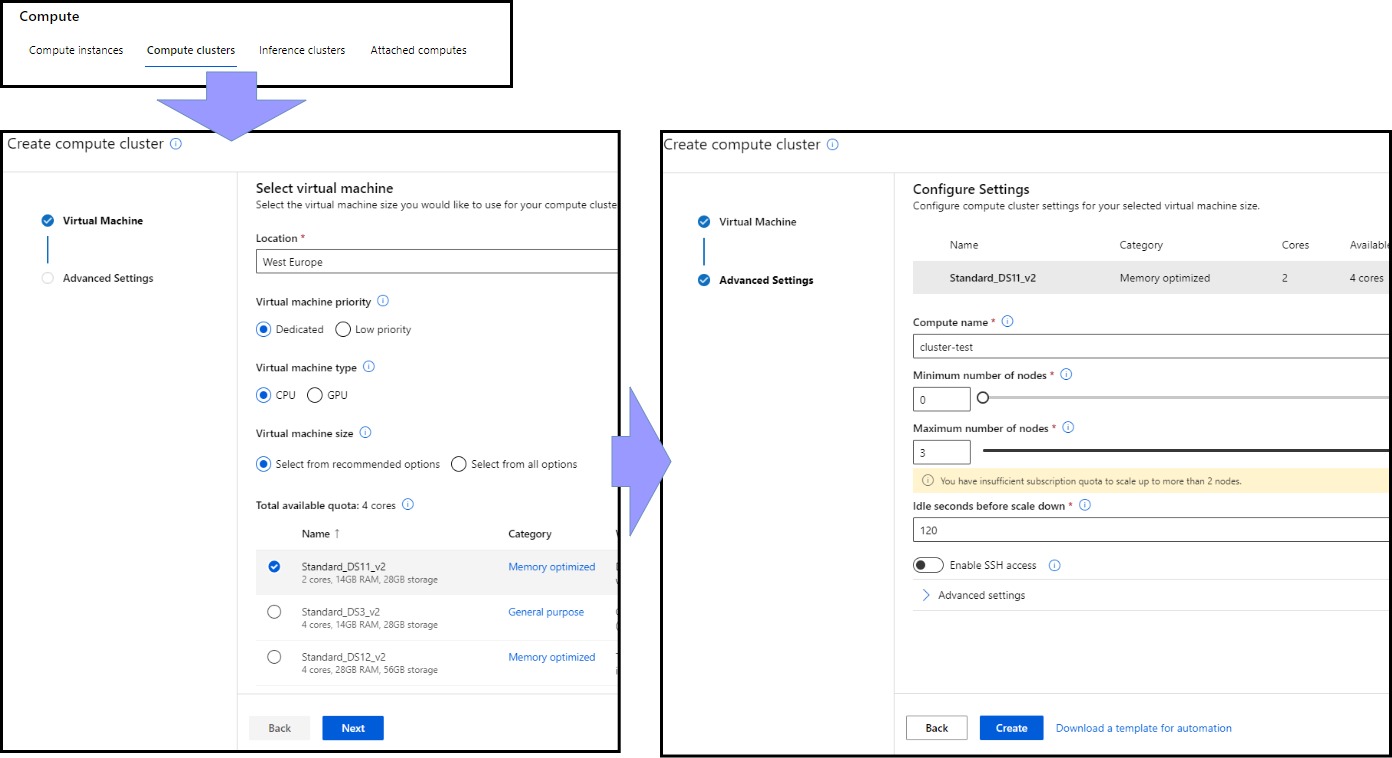
Compute Clusters are required when implementing Automated Machine Learning Experiments.
There are two additional computation options available in Azure Machine Learning;
Inference Clusters create a Docker container that hosts the model and associated resources needed to use it. This container is then used in a compute target to host the ML model.
Attach Computes make it possible to attach Databricks, Data lake Analytics, HDInsight or a prevailing VM as a compute for your workspace, and thus will not be managed by Azure Machine Learning.