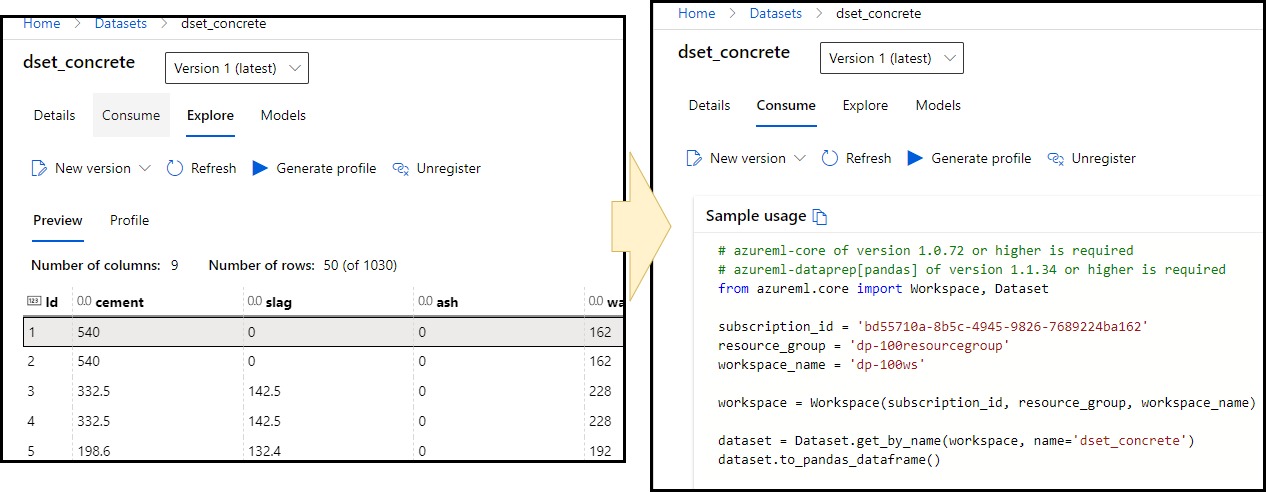
Introduction
In AzureML, the two essential concepts that help us work with data are Datastores and Datasets.
- Datastores are used for storing connection information to Azure storage services
- Datasets are references to the location of the data source.
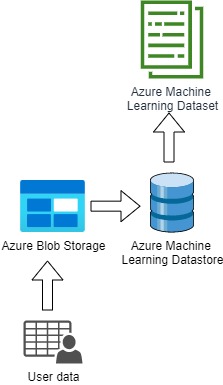
Datastores
Azure has various locations for storing data, such as;
- Azure Blob Storage
- Azure SQL Database
- Azure Datafactory
- Azure Databricks
These are the places where the data can exist.
An Azure storage account is a container for all the Azure Storage data objects blobs, file shares, queues, tables, and disks, making them accessible from anywhere in the world over HTTP or HTTPS.
When we create an AzureML resource, an associated storage account is also created. This account will contain two built-in datastores;
- an Azure Storage Blob Container and
- an Azure Storage File Container
These will contain the relevant data and code for the AzureML resource.
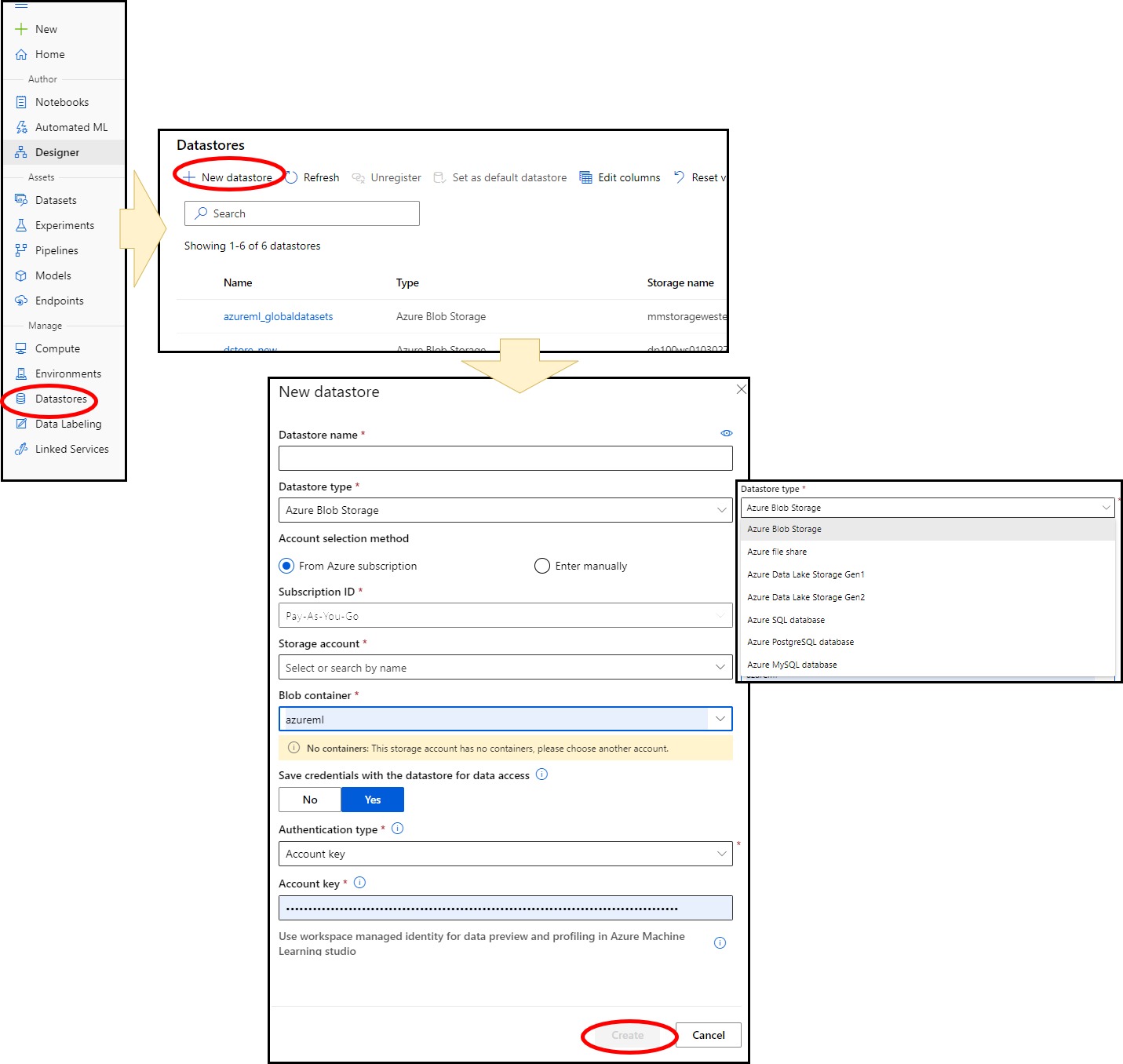
Datasets
Datasets are those assets in the Machine learning Workspace where we connect to the data in storage services so that the data is made available for ML Experiments. Hence when creating a dataset, we create a reference to the data in storage services. Information is not copied from the storage service to the workspace for several reasons.
- It is easier to access the data in the workspace
- Data can be registered once and used for many experiments
- Data is traceable; we know where it is being used
- Data objects are versioned
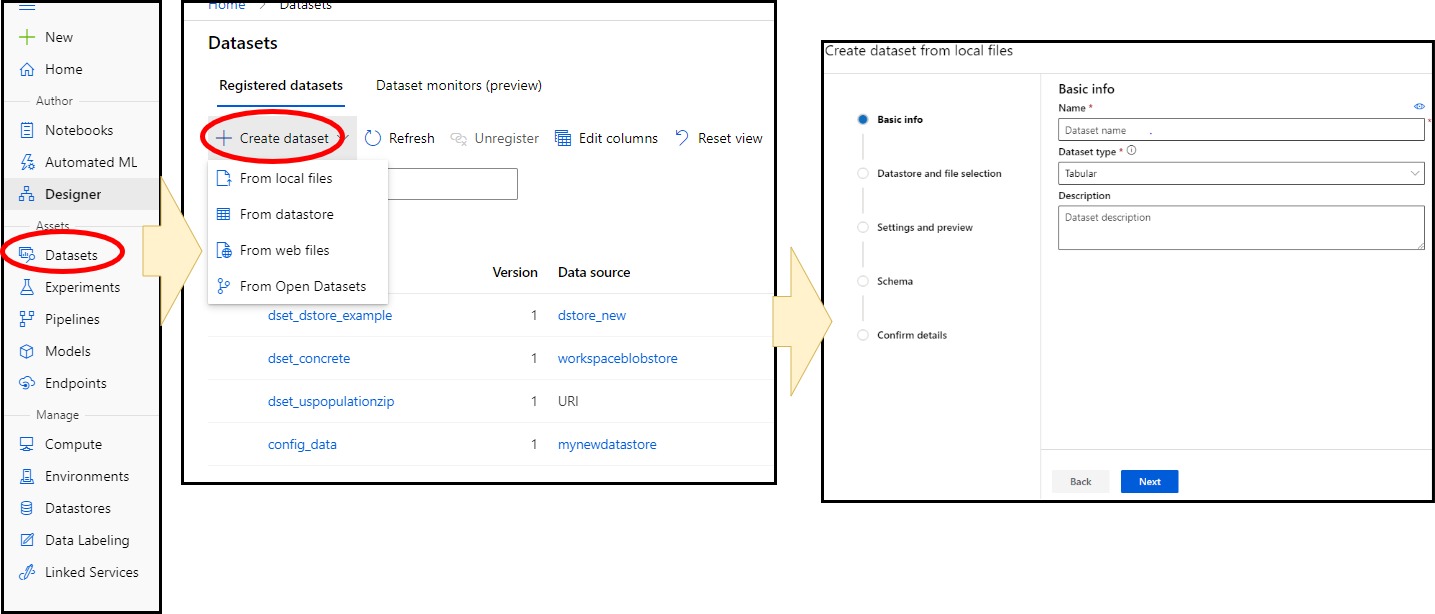
Datasets are created in a number of ways.
- Upload from a local file. This method will also create a datastore for the file.
- From a Datastore
- From a web file, i.e. a file hosted on the web via a URL
Datasets can be
- Tabular, structures data that is easily used in libraries such as Pandas
- File, Unstructured data that is a collection of file paths