In this post, we will validate the implementation of the Karnik-Mendel algorithm found in the type-2 fuzzy logic library with a worked example available in Mendel’s book “Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic systems."
The example calculates the centroid of interval type-2 fuzzy sets with uncertain means m∈[m1,m2], where the UMF and LMF of the set are calculated as follows:
| exp[−0.5×(x−m1σ)2] | ,x<m1 | |
| UMF(˜A)= | 1 | ,m1,≥x≥m2 |
| exp[−0.5×(x−m2σ)2] | ,x>m2 |
LMF(˜A)=min(exp[−0.5×(x−m1σ)2],exp[−0.5×(x−m2σ)2])
[5,5],
[4.875, 5.125],
[4.75, 5.25],
[4.625, 5.375],
[4.5, 5.5],
[4.25, 5.75],
[4,6],
[3.75, 6.25],
[3.5, 6.]
Note that the first case, where m1=m2=5 will produce a type-1 fuzzy set.
The following python code is used to create the sets. As the sigma value is specified to be 1, it is not passed as a parameter in the generation function. The function expects the m-values as parameters and returns an IntervalType2FuzzySet class that contains CrispSet values having UMF and LMF for each primary domain value.
def generate_set_uncertain_mean(m_1:int, m_2:int) -> ItervalType2FuzzySet:
'''
Generates an interval type-2 fuzzy set with uncertain mean as
specified by Jerry Mendel in his book. The set has LMF and UMF
constructed from two Gaussian functions with fixed standard
deviation and uncertain means that takes values in [m1. m2].
Arguments:
----------
m_1 - lower mean value
m_2 - upper mean value
Returns:
--------
it2fs - Interval type-2 fuzzy set
Reference:
----------
Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic systems:
Introduction and new directions-Jerry M. Mendel;
Prentice-Hall, PTR, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2001,
555pp., ISBN 0-13-040969-3., page 91
'''
# function to calculate UMF and LMF
sigma=1
u_A = lambda x,m: exp((((x-m)/sigma)**2)*-0.5)
# range of primary domain
primary_domain = np.linspace(0, 10, 101)
it2fs = IntervalType2FuzzySet()
for x_val in primary_domain:
if x_val < m_1:
it2fs.add_element(
x_val,
CrispSet(
u_A(x_val, m_2),
u_A(x_val, m_1))
)
elif x_val >m_2:
it2fs.add_element(
x_val,
CrispSet(
u_A(x_val, m_1),
u_A(x_val, m_2))
)
else:
it2fs.add_element(
x_val,
CrispSet(
min(u_A(x_val, m_2), u_A(x_val, m_1)),
1)
)
return it2fs
When calculating the centroids, Mendel produces the following result in his book:
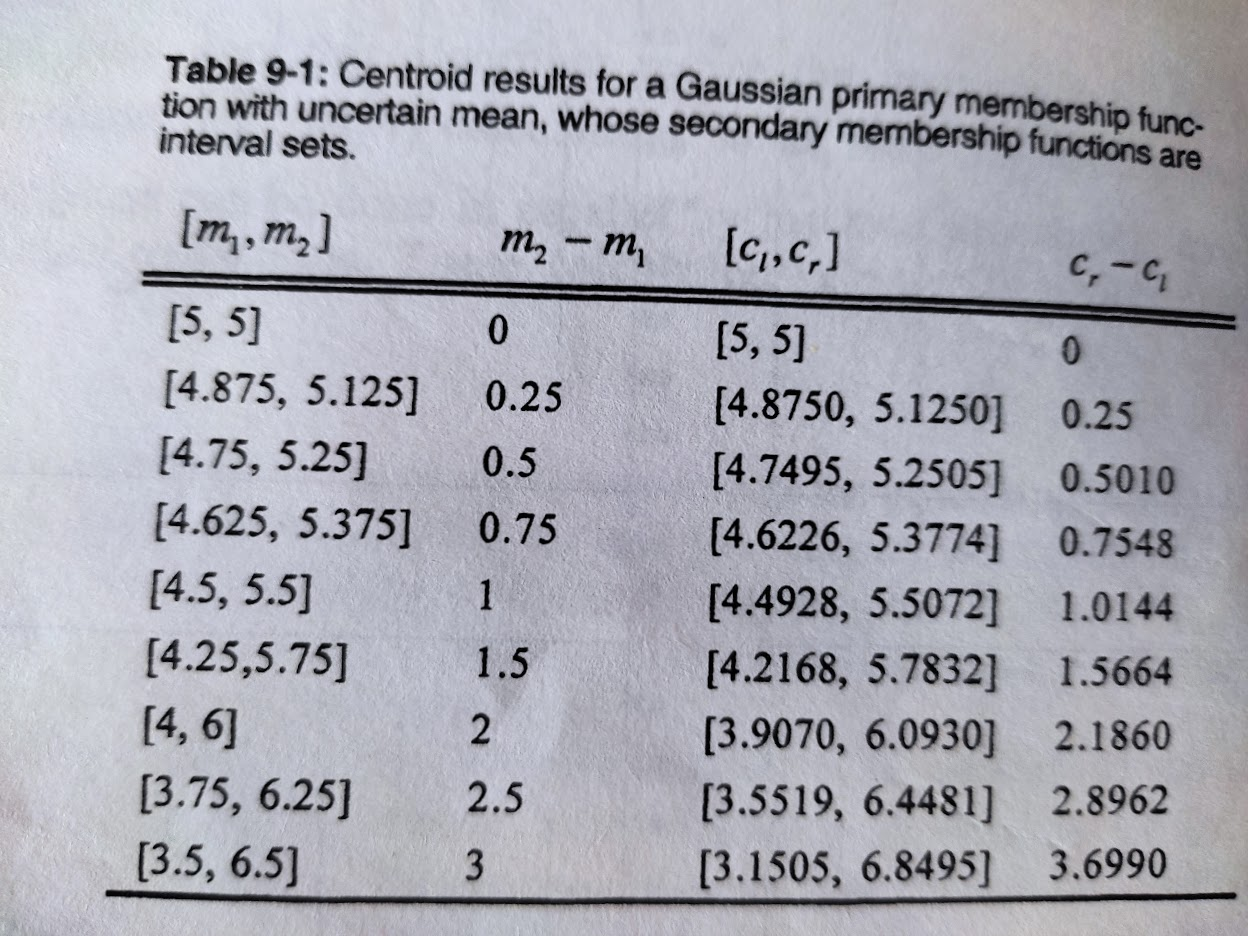
The next step is replicating this result using the type-2 fuzzy logic library. We will use the following classes in this exercise.
- The it2_kernikmendel_reduce function in the type_reduction module to calculate the centroids
- The SetPlotter class found in the display module is used to plot the sets used in this exercise
- We will also use the PrettyTable module so that the results can be displayed properly
The code used to generate and plot the sets and calculate the centroids is below:
def mendel_example_9_4():
'''
Computation of centroid of interval type-2 fuzzy sets
having Gaussian primary membership function with uncertain mean,
m \in [m1, m2] with the following values:
[5,5],
[4.875, 5.125],
[4.75, 5.25],
[4.625, 5.375],
[4.5, 5.5],
[4.25, 5.75],
[4,6],
[3.75, 6.25],
[3.5, 6.]
Note that the case where m1=m2=5 is the type-1 set.
Arguments:
----------
Returns:
--------
Reference:
----------
Uncertain rule-based fuzzy logic systems:
Introduction and new directions-Jerry M. Mendel;
Prentice-Hall, PTR, Upper Saddle River, NJ, 2001,
555pp., ISBN 0-13-040969-3. page 261
'''
# results table
table = PrettyTable()
table.field_names=['[m1, m2]', 'm2-m1', '[cl, cr]', 'cr-cl']
# Setplotter from type-2 fuzzy library to plot sets
set_plotter = SetPlotter()
# ranges specified in the text
m_pairs = [
(5,5),
(4.875, 5.125),
(4.75, 5.25),
(4.625, 5.375),
(4.5, 5.5),
(4.25, 5.75),
(4,6),
(3.75, 6.25),
(3.5, 6.5)
]
for m1, m2 in m_pairs:
# create set
i_set = generate_set_uncertain_mean(m1, m2)
# find its centroid
cen = it2_kernikmendel_reduce(i_set)
table.add_row([
f'[{m2}, {m1}]',
m2-m1,
f'[{cen.right}, {cen.left}]',
round(cen.left-cen.right, 4)
])
# add set to plt
set_plotter.add_invervaltype2set(i_set, f'[{m2}, {m1}]')
print(table)
set_plotter.plot(5)
plt.show()
Results
We generated the following plots to illustrate the interval type-2 sets produced. As expected, the first example had a type-1 set.
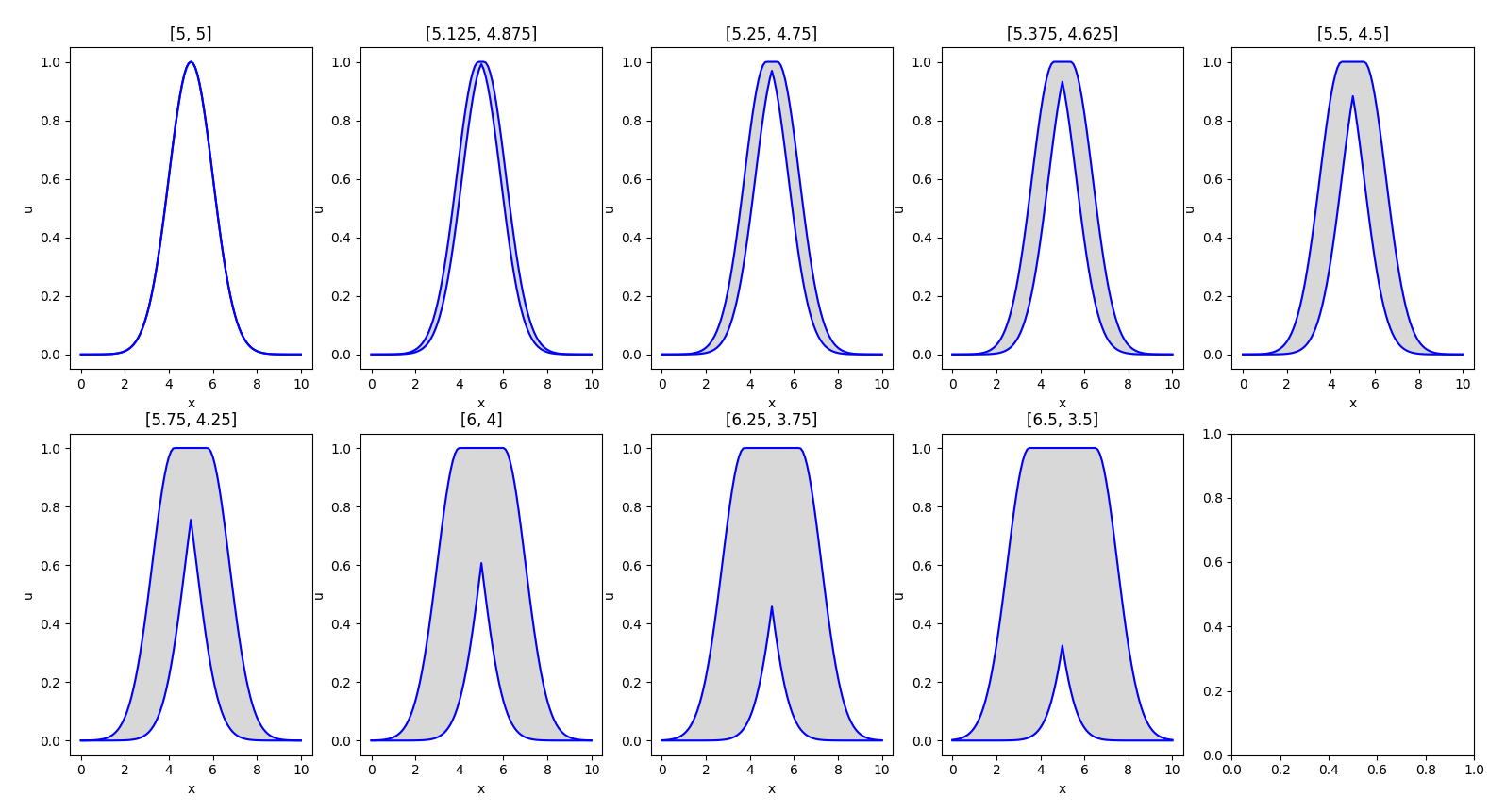
The centroid results match those obtained by the author:
+----------------+-------+--------------------+--------+
| [m1, m2] | m2-m1 | [cl, cr] | cr-cl |
+----------------+-------+--------------------+--------+
| [5, 5] | 0 | [5.0, 5.0] | 0.0 |
| [5.125, 4.875] | 0.25 | [4.87498, 5.12502] | 0.25 |
| [5.25, 4.75] | 0.5 | [4.74952, 5.25048] | 0.501 |
| [5.375, 4.625] | 0.75 | [4.62265, 5.37735] | 0.7547 |
| [5.5, 4.5] | 1.0 | [4.49285, 5.50715] | 1.0143 |
| [5.75, 4.25] | 1.5 | [4.21675, 5.78325] | 1.5665 |
| [6, 4] | 2 | [3.90697, 6.09303] | 2.1861 |
| [6.25, 3.75] | 2.5 | [3.55194, 6.44806] | 2.8961 |
| [6.5, 3.5] | 3.0 | [3.15053, 6.84947] | 3.6989 |
+----------------+-------+--------------------+--------+